According to Eurostat[1], european website for statistics, the amount of waste electrical and electronic equipment (known as WEEE or e-waste) generated every year since 2018 data in the EU is increasing. The figure shown below shows the increasing data evolution for all European countries and also for the specific countries which are part of the consortium of this project.
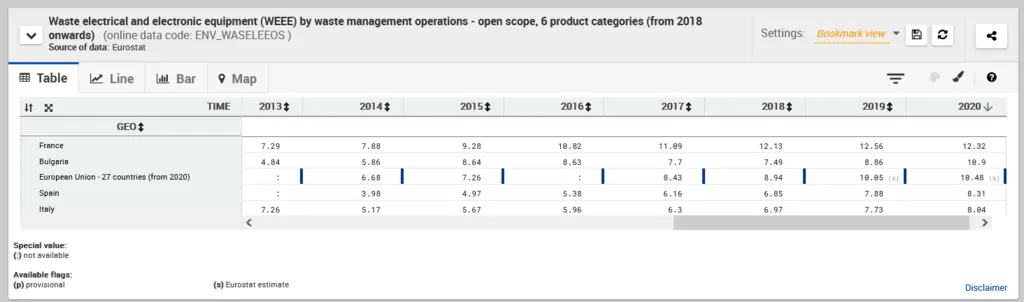
Why are these numbers growing?
According to the European Commission[3], this waste is coming from electrical and electronic equipment including a large range of devices such as computers, fridges, and mobile phones at the end of their life.
This type of waste contains a complex mixture of materials, some of which are hazardous. These can cause major environmental and health problems if the discarded devices are not managed properly. In addition, modern electronics contain rare and expensive resources, which can be recycled and reused if the waste is effectively managed.
Thus, improving the collection, treatment, and recycling of electrical and electronic equipment at the end of their life can:
- Improve sustainable production and consumption
- Increase resource efficiency
- Contribute to the circular economy
To reach these objectives, the European Union has introduced the WEEE Directive[4] and the RoHS Directive[5] to tackle the issue of the growing amount of waste.
The WEE Directive lays down measures to protect the environment and human health by preventing or reducing the adverse impacts of the generation and management of waste from electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) and by reducing overall impacts of resource use and improving the efficiency of such use in accordance with Articles 1 and 4 of Directive 2008/98/EC, thereby contributing to sustainable development.
The RoHS Directive lays down rules on the restriction of the use of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) with a view to contributing to the protection of human health and the environment, including the environmentally sound recovery and disposal of waste EEE.
References
[1] Eurostat website.
https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat.
Accessed on 05/09/2023.
[2] Eurostat statistics.
https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/ENV_WASELEEOS__custom_5812085/bookmark/table?lang=en&bookmarkId=80d92bc0-09c4-4b6c-bd8b-fc4245ca69ee.
Accessed on 05/09/2023.
[3] European Commission: Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE).
https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/waste-and-recycling/waste-electrical-and-electronic-equipment-weee_en.
Accessed on 05/09/2023.
[4] WEEE Directive.
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:02012L0019-20180704.
Accessed on 05/09/2023.
[5] RoHS Directive.
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:02011L0065-20160715.
Accessed on 05/09/2023.
